Infrastructure Utilisation and Healthcare Capacity
NHS appointment data and resource allocation and patient experience
Project Overview
NHS stakeholders sought clarity on use of staff and healthcare infrastructure to guide strategic decisions regarding expanding or optimizing existing structures. 137,792 appointment records were analyzed over 11 months to answer two critical business questions:
1. Has there been adequate staff and structure use across NHS networks?
2. What is the actual utilisation of NHS healthcare resources?
The analysis also incorporated social media X comments in evaluating patient perception of NHS services.
Toolkit
Python (Jupyter Notebook)
Data analysis and visualization
Pandas & NumPy libraries
Data cleaning, exploration, aggregation, and statistical analysis
Matplotlib & Seaborn libraries
Advanced data visualization for pattern identification
Methodology
1
Data Import & Quality Assessment
Three distinct datasets were imported and comprehensive exploratory data analysis (EDA) was performed. Data quality was evaluated, and analytical opportunities were identified. Unknown or unmapped categories were identified along with temporal gaps that could affect trend analysis.
2
Pattern Analysis
Deep-dive EDA was conducted to detect seasonal trends and monthly appointment patterns. Appointment data was analyzed across different features: Service Setting, National Category, Appointment Status (including DNAs), Appointment Mode, Wait Times Between Booking and Appointment, Regional Distribution, and Appointment Duration. This multi-dimensional analysis revealed critical bottlenecks and opportunities for efficiency.
3
Sentiment Analysis
Social media X comments were analyzed along with relevant hashtags to detect patient sentiment and identify significant complaints. This qualitative analysis complemented the quantitative appointment data, providing a complete picture of patient experience and perception of NHS services.
4
Synthesis
Synthesized findings from appointment data and sentiment analysis to answer stakeholder questions about capacity, staff adequacy, and resource utilization. Actionable recommendations were developed prioritizing potential impact and feasible implementation.
Total Appointments per Month
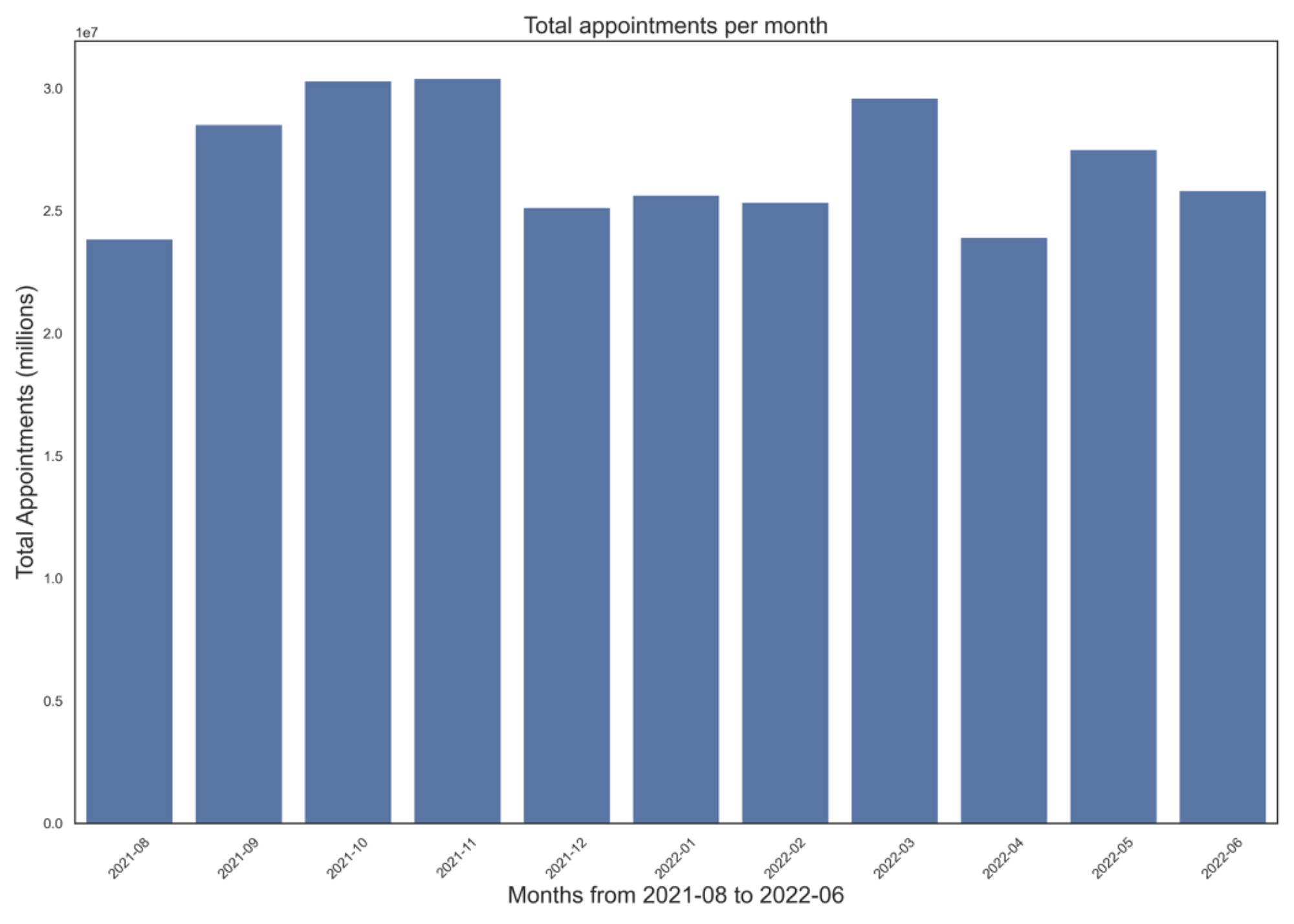
Monthly appointment volume across the NHS network (August 2021 - June 2022)
Key Insights
-
Data Quality Challenges• Many variables contained 'unknown' or 'unmapped' entries, compromising analysis integrity in certain areas
• 11-month temporal window provided insight regarding seasonal trends. A longer time span would strengthen confidence in reliable patterns
-
Scheduling Inefficiencies• Significant number of DNAs (Did Not Attend) appointments identified across the network
• Long wait times between booking and appointments, especially during peak periods
• Inefficiencies represent substantial opportunities for capacity optimization without infrastructure expansion
• Face-to-face appointments were roughly double in volume compared to telephone appointments -
Seasonal Demand Patterns• Clear seasonal trends emerged in appointment demand
• Appointments peaked in Autumn and March, suggesting correlation with holiday periods and seasonal illnesses
• Understanding these patterns enables proactive resource planning and staff deployment strategies
• Predictable fluctuations offer opportunities for dynamic capacity management -
Patient Sentiment Insights• Social media analysis X revealed patient concerns about waiting times
• Sentiment analysis provided context for quantitative findings about DNAs and booking delays
• Patient feedback indicates communication gaps that could be addressed through digital solutions
Business Recommendations
1
Implement dynamic staff models
Use peak-month forecasts to deploy staff where needed most. Historical patterns show predictable demand surges in Autumn and March that could be addressed through flexible staffing arrangements rather than permanent infrastructure expansion.
2
Leverage patient communication tools
Reduce DNAs through automated reminders, SMS notifications, or digital rebooking options. Even a modest reduction in missed appointments could free significant capacity without additional resources.
3
Expand use of remote consultation modes
Promote telephone or video consultations when clinically appropriate. With face-to-face appointments at double the volume of remote options, strategic shifting could ease facility pressure and improve patient satistacftion.
4
Establish continuous monitoring framework
Track data on any implemented changes to monitor how improvements are perceived and utilized by patients. Create feedback loops linking operational changes to patient sentiment for evidence-based optimization.
Appointments and NHS Services Utilisation
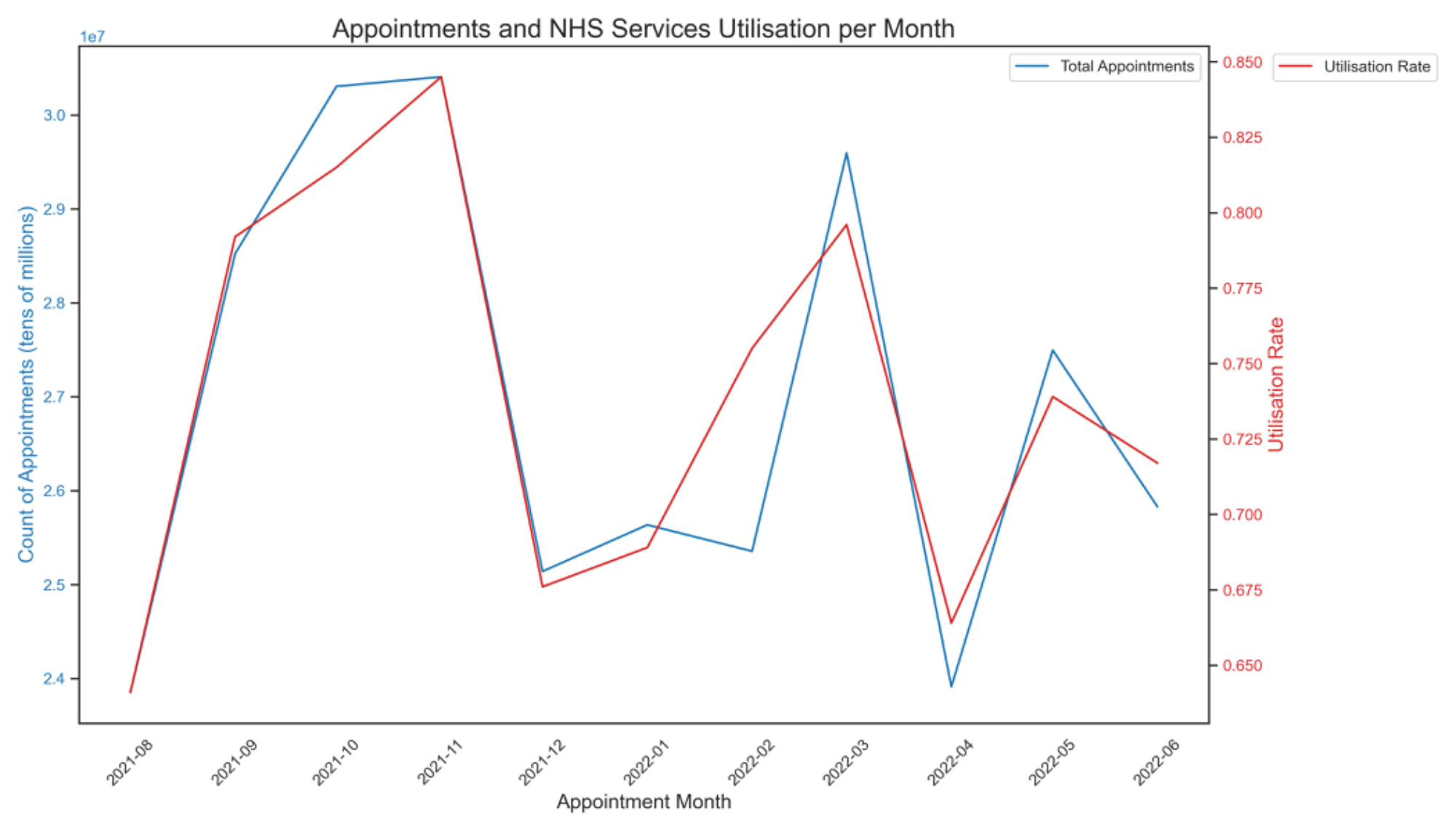
Relationship between total appointments and service utilisation rate over time
Download Project Files
Access the complete analysis report and Jupyter notebook with full code implementation.